 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?  Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a critical cytokine in adoptive cell therapy that plays a critical role in driving the activation and proliferation of immune cells. Its role is particularly prominent in Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TIL), Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T cells, and Natural Killer (NK) cell ex vivo expansion. Despite its universal use as a growth factor in various immune cell expansion protocols, its optimization is essential in finding the line between positive therapeutic outcomes and mitigating any associated toxicities.
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) plays an essential role the activation and proliferation of TILs, which are immune cells that have already infiltrated tumors and orchestrate anti-tumor immune responses from within. The combination of TIL therapy and IL-2 is believed to enhance the anti-tumor effect, providing a sustained responses in certain patients. For instance, a Phase I trial combining TIL adoptive cell therapy (ACT) with dendritic cell (DC) vaccination in metastatic melanoma patients demonstrated complete responses in certain individuals, with ongoing responses lasting over 18 months. This TIL therapy process involves harvesting T cells from a patient’s tumor tissue and selecting those with the ability to recognize certain tumor antigens. These selected TILs undergo rapid ex vivo activation and expansion with IL-2 before reintroduction into the patient.
Harvesting TILs starts from isolating TILs from excised tumor tissue blocks and using a rapid expansion protocol (REP) for in vitro amplification. To mitigate T-cell damage, dividing the tumor block into small 1mm3 pieces and culturing them in a high-dose IL-2 medium for two weeks is suggested. To expedite the in vitro cultivation period while maintaining TIL efficacy, researchers have introduced high doses of IL-2, anti-CD3 antibodies, and PBMC feeder cells into the rapid expansion process. However, the need for frequent IL-2 supplementation every few days poses a logistical challenge when manufactured at scale. Moreover, there are concerns about the potential differentiation of TILs, which could compromise their clinical efficacy. Future strategies are aimed at refining TIL therapy protocols and improving patient outcomes in the fight against cancer. This includes alternative ex vivo expansion methods, using cytokines such as IL-15 and IL-21, co-stimulatory molecules, and immune checkpoint inhibitors, to stimulate TIL amplification and minimize unwanted differentiation.
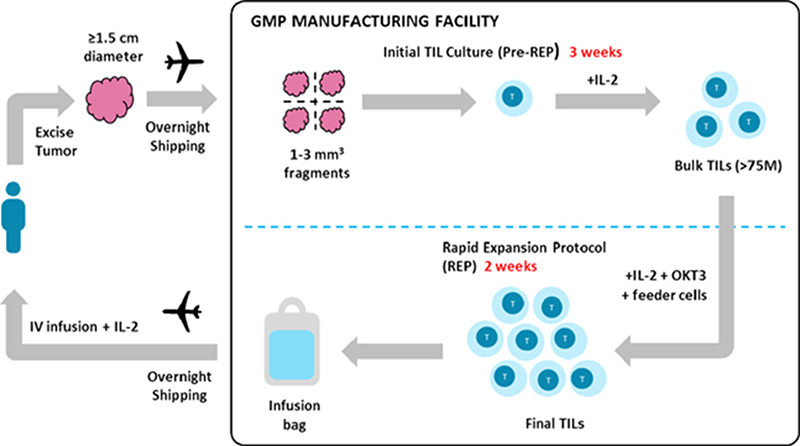
Development of TIL Therapy Under IL-2 Conditions
CAR-T cell expansion relies heavily on IL-2 as a primary cytokine driving robust T cell proliferation essential for ex vivo clinical production. Originally identified as a T-cell growth factor, IL-2 marked a groundbreaking discovery due to its indispensable role in triggering T cell proliferation. In CAR-T cell therapy, T cells harvested from patients first undergo genetic modification to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), before undergoing expansion to the required cell doses for cell therapy use.
With growing recognition of the importance of persistent memory T cells in cancer treatment, the mainstream approach involves co-culturing of T cells with IL-2 with other growth factors. Combinations of IL-7 and IL-15 emerged as a notable cytokine ‘cocktail’, preserving the T memory stem (Tscm) phenotype while augmenting CAR-T cell cytotoxicity against tumors. Furthermore, the synergistic combination of IL-21 with IL-7 or IL-15 stimulates CD8+ T cell proliferation and fosters IFN-γ production, thus fortifying the cytotoxic potential of these immune effectors. Impressively, IL-21 also showcases promise in driving the in vitro differentiation of Tscm cells, enriching the therapeutic arsenal against cancer.
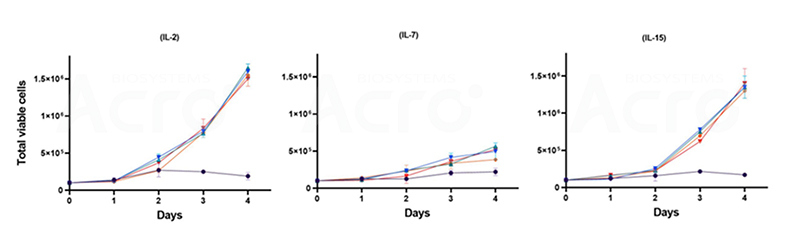
The growth kinetics of T cells under the stimulation of single cytokines doses (IL-2, IL-7, & IL-15) Cytotherapy, 23(5), S177. (2021).
However, the immune cell expansion trend is beginning to shift away from the conventional addition of IL-2 during cell cultures. Despite its indispensable nature for T cell function, its systemic administration poses a challenge due to severe toxicity risks. To navigate this obstacle, researchers have innovated an orthogonal IL-2 and IL-2 receptor systems designed to selectively expand CAR-T cells, allowing for systemic delivery of IL-2 while mitigating off-target toxicity. This approach exhibits considerable potential in preclinical models, bolstering CAR-T cell expansion and heightening their antitumor efficacy with minimized risk for IL-2 toxicity.
Ex vivo expansion of NK cells is also reliant on IL-2, essential for driving their activation and proliferation. However, IL-2 alone often falls short in achieving substantial NK cell expansion in vitro. To overcome this limitation, researchers have turned to combinatorial approaches, particularly with cytokines like IL-15 and IL-21, renowned for their synergistic effects. Synergistic combination of IL-2 with IL-15 and IL-21 has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in fueling NK cell expansion, resulting in heightened cytotoxicity and sustained secretion of key anti-tumor cytokines, most notably IFN-γ and TNF-α.
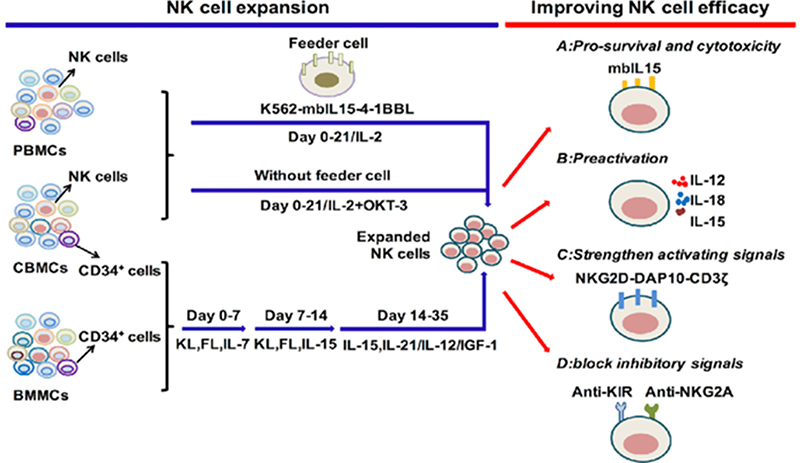
Cytokine regulation of NK cell expansion and cytotoxicity.
Preclinical melanoma models have provided compelling evidence of the efficacy of this enhanced NK cell expansion and activation method. Furthermore, ongoing investigations aim to elucidate the optimal cytokine cocktail for maximizing NK cell expansion, fine-tuning their cytotoxic capabilities for precision cancer immunotherapy. Thus, IL-2, in concert with select cytokines, emerges as a fundamental tool in NK cell expansion, fostering their potent antitumor activity and unlocking their full therapeutic potential in immunotherapy.
IL-2 stands as pivotal cytokine in cell therapy, driving immune cell activation and proliferation crucial for effective anti-tumor responses in TIL, CAR-T, and NK cell therapies. It expands TILs for tumor targeting, enhances CAR-T cell cytotoxicity, and synergizes with other cytokines to boost NK cell activity. Despite toxicity challenges, innovative approaches like orthogonal IL-2 systems promise to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing risks, highlighting IL-2's essential role in shaping immune cell therapy for precision cancer treatment.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.