 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?  Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
> Insights > [Inspiring Target] IL-4R Alpha, a Potential Drug Target Worth over $10 Billion 
Interleukin-4 receptor (IL-4R) has emerged as an ‘inspiring’ target for innovative therapies aimed at treating atopic diseases. This type-1 transmembrane protein plays a key role in the molecular pathway that drives a specific immune response pattern called type-2 inflammations. These inflammations are the root cause of several medical conditions including atopic dermatitis (AD) and certain types of asthma. A brief understanding the molecular pathway behind this immune response pattern is fundamental to elucidating the mechanism of drug action and recognizing the immense potential behind IL-4R alpha targeting drugs.
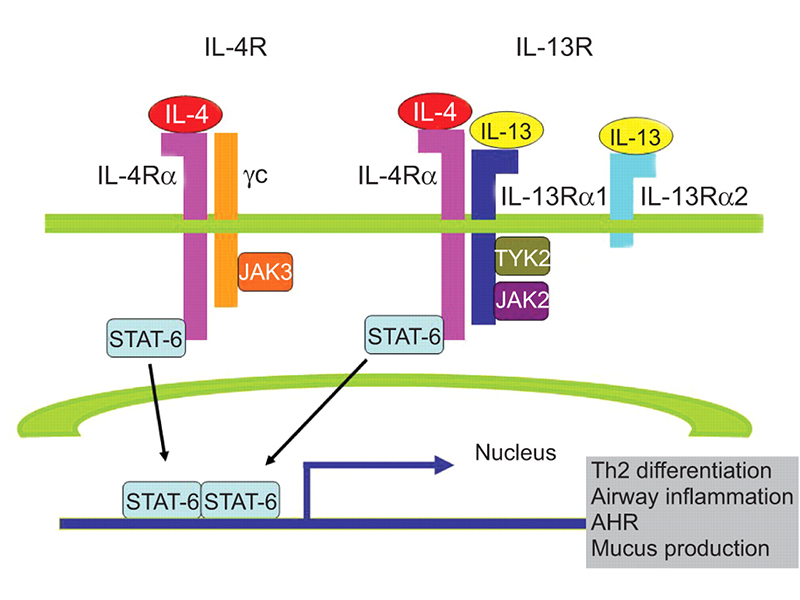
IL-4R cellular pathway
IL-4 and IL-13 are cytokines that have diverse biological and immunological effects on B-lymphocytes, monocytes, dendritic cells, and fibroblasts’ adjustment function. These cytokines bind to IL-4R alpha and IL-13R alpha to initiate the type-2 inflammation pathway that includes differentiation of Th2 cells, airway inflammation, and mucus production. In cases of allergic diseases such as AD, the type-2 inflammation pathway is first initiated by an abnormal secretion of cytokines stemming from an imbalance of Th1 and Th2 differentiation. Activated Th2 cells release cytokines including IL-4, 13, and 31, which activate downstream B cells to transform and produce IgE antibodies. In turn, mast cells and basophils are recruited to degranulate and produce inflammatory factors. Simultaneously, the secreted IL-4 and 13 continue to bind to its respective receptors (e. g. IL-4R) that repeatedly promotes TH2 differentiation and subsequent inflammation.
The signaling role of IL-4 and IL-13 in the type-2 inflammation pathway reveals IL-4R alpha as a prospective target for patients with abnormal type-2 inflammation responses. Unlike the single-target functions of drugs targeting IL-4 and IL-13 specifically, IL-4R alpha has an innovative mechanism similar to ‘bi-specific’ targets. Antibodies targeting IL-4R alpha prevents the binding of both IL-4 and IL-13 which blocks intracellular signaling, thereby regulating immune function through inhibition of Th2 cell differentiation, IgE synthesis, and inflammatory substances secretion. As a result, many pharmaceutical companies around the world have emphasized the development of IL-4R targeting-drugs in their pipelines.
Advances in drug research and development targeting IL-4R alpha (Sourced from Pharmacodia)
| Drug Name | Highest Stage | Company | Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dupilumab | Launched (2017) | Sanofi/Regeneron | Eosinophilic Esophagitis; Atopic Dermatitis; Sinusitis; Nasal Polyps; Asthma |
| CM-310 | Phase III | Keymed Biosciences CSPC Pharmaceutical | Sinusitis; Nasal Polyps; Atopic Dermatitis; Pruritus; Solid Tumors; Asthma; Nasal Disorders; Allergic Rhinitis |
| Recombinant anti-IL-4Rα humanized monoclonal antibody | Phase II | Sunshine Guojian | Atopic Dermatitis |
| MG-K10 | Phase II | MABGEEK Dragon Boat Pharmaceutical | Atopic Dermatitis; Asthma |
| Manfidokimab | Phase II | Akeso Pharmaceuticals | Atopic Dermatitis; Asthma |
| QX-005N | Phase II | Qyuns Therapeutics | Atopic Dermatitis; Prurigo; Asthma; Chronic Urticaria; Sinusitis |
| Elarekibep | Phase II | AstraZeneca Pieris Australia Pty Ltd | Asthma |
| CBP-201 | Phase II | Connect Biopharma | Atopic Dermatitis; Asthma |
| SHR-1819 | Phase I | Atridia Pty Ltd; Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals | Atopic Dermatitis; Asthma |
| LQ-036 | Phase I | Shanghai Novamab Biopharmaceuticals; Syneos Health | Asthma |
| BA2101 | Preclinical | Boan Biotech | Atopic Dermatitis; Asthma; Sinusitis;Itching; Hives |
Currently, the only IL-4R alpha targeting drug available on the market is Dupilumab, which was jointly developed by Sanofi and Regeneron. In 2020, sales for Dupilumab exceeded $4 billion, with projections of over $10 billion by 2024. One of the main targets for Dupilumab is AD, otherwise known as eczema, which is a prevalent disease that affects millions of people. According to epidemiologic statistics from Frost & Sullivan, the number of patients suffering from AD has reached 649 million and is predicted to increase to 755 million people globally. Current first-line treatment for moderate-to-severe AD involves the use of topical creams and ointments to manage the severity of itching. However, for patients with uncontrolled AD, Dupilumab manages the inflammation before it even begins by inhibiting the inflammation signaling pathway. Its effectiveness has resulted in a multi-disciplinary consensus statement that emphasizes the use of Dupilumab as a first-line systemic treatment modality when topical therapy is ineffective. The success of Dupilumab in controlling severe cases of AD has helped broaden its clinical applications into other medical conditions including eosinophilic esophagitis, sinusitis, and certain cases of asthma.
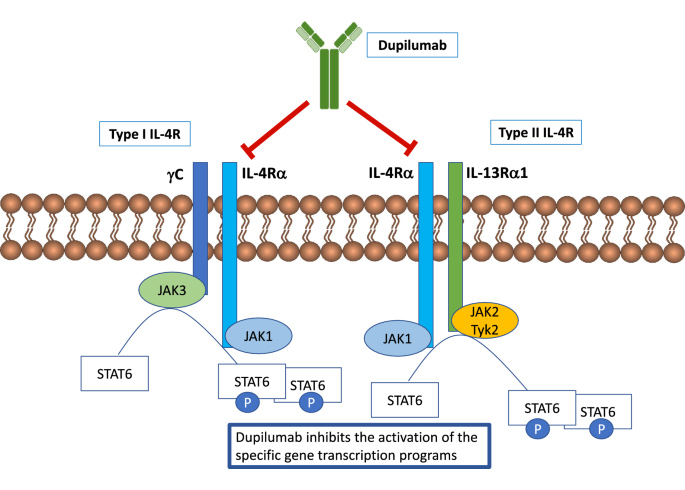
Mechanism of Action of Dupilumab
Overall, IL-4R alpha is an extremely promising therapeutic target for the management and treatment of atopic diseases. ACROBiosystems has specially launched a series of IL-4R alpha/ IL-4/ IL-13 recombinant proteins, which are suitable for antibody screening and functional verification, to support the research and development of IL-4R alpha targeted drugs.
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Species | Product Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-4 R alpha | ILR-H5221 | Human | Human IL-4 R alpha / CD124 Protein, His Tag |
| ILR-H82E9 | Human | Biotinylated Human IL-4 R alpha / CD124 Protein, Avitag™, His Tag | |
| ILR-H5253 | Human | Human IL-4 R alpha / CD124 Protein, Fc Tag | |
| ILR-H82F4 | Human | Biotinylated Human IL-4 R alpha / CD124 Protein, Fc, Avitag™ | |
| ILR-M5252 | Mouse | Mouse IL-4 R alpha / CD124 Protein, Fc Tag | |
| ILR-M52H1 | Mouse | Mouse IL-4 R alpha / CD124 Protein, His Tag | |
| ILR-C5258 | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque IL-4 R alpha / CD124 Protein, Fc Tag | |
| ILR-C52H8 | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque | Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque IL-4 R alpha / CD124 Protein, His Tag | |
| IL-4 | IL4-H4218 | Human | ActiveMax® Human IL-4 Protein, Tag Free |
| IL4-H82E0 | Human | Biotinylated Human IL-4 Protein, Avitag™, His Tag | |
| IL4-H52H9 | Human | Human IL-4 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) | |
| IL4-M52H5 | Mouse | Mouse IL-4 Protein, His Tag | |
| IL4-C5259 | Cynomolgus | Cynomolgus IL-4 Protein, Fc Tag (MALS verified) | |
| IL-13 | IL3-H52H4 | Human | Human IL-13 Protein, His Tag |
| IL3-H5256 | Human | Human IL-13 Protein, Fc Tag | |
| IL3-H82E5 | Human | Biotinylated Human IL-13 Protein, His, Avitag™ | |
| IL3-C52H4 | Canine | Canine IL-13 Protein, His Tag |
1. C. K. Oh, G. P. Geba, N. Molfino. Investigational therapeutics targeting the IL-4/IL-13/STAT-6 pathway for the treatment of asthma. European Respiratory Review 19, 46-54 (2010). DOI: 10.1183/09059180.00007609
2. Licari, A., Castagnoli, R., Marseglia, A. et al. Dupilumab to Treat Type 2 Inflammatory Diseases in Children and Adolescents. Pediatr Drugs 22, 295–310 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40272-020-00387-2.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.