Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?  Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
In Jan 2020, the sudden emergence of a previously unknown, highly contagious respiratory pathogen launched a global pandemic that remains circulating today. The SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus that causes COVID-19 has surpassed 211 million infections worldwide within twenty months of the pandemic, resulting in more than four million deaths until August 2021 (Coronavirus Resource Center, 2021). Not since 1918 has the world been so affected by the emergence, spread, and death toll resulting from a respiratory virus that impacted on not only global public health but also the economic status of nations and individuals. This devastating public health emergency called for a comprehensive response that required the joint effort of pharmaceutical, biotech, and academic collaborators to develop prevention and treatment approaches for this new disease.
This article is a reflection of COVID-19, following some possible solutions for related research, vaccine and diagnostics development.
• What we have achieved in the fight against COVID-19
• What remains unknown about the virus
• What ACRO offer
ACROBiosystems is dedicated to aid the global COVID-19 response. As a leading life science supplier, we remain steadfast in our mission to support researchers, developers and manufacturers with key reagents to better address the persisting public health concerns. As such, we have consolidated our product and service offerings to a comprehensive solution for SARS-CoV-2, which meet customers' need in both the detection of COVID-19 and the development of vaccines and therapies. As SARS-CoV-2 continues to spread and evolve, our top priority is to provide support to rapidly respond to the challenges. Now, more than ever, we are mobilizing forces to keep the circulating and emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants under surveillance and develop products targeting the Variants of Concerns (VOCs) in the timeliest manner. Our product pipeline includes multiple recombinant antigen mutants, broadly neutralizing antibodies, ELISA kits with high sensitivity and protein-pre-coupled magnetic beads that support high-throughput applications.
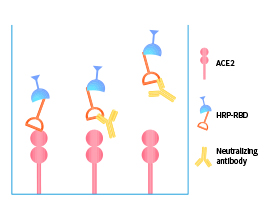
>>> Featured products: VOCs-specific neutralizing antibody serological titer kits
| Lineage | Cat. No. |
|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2 (U.K) Alpha | B.1.1.7 | RAS-N028 |
| SARS-CoV-2 (South Africa) Beta | B.1.351 | RAS-N031 |
| SARS-CoV-2 (Brazil) Gamma | P.1 | RAS-N034 |
| SARS-CoV-2 (India) Delta | B.1.617.2 | RAS-N040 , RAS-N041 |
>>> Featured products: VOCs-specific neutralizing antibody serological titer kits
| Cat.No. | Product Description | Application | Preorder/Order |
|---|---|---|---|
| MBS-K001 | SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1-coupled Magnetic Beads | S1 protein antibody screening | |
| MBS-K002 | SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD-coupled Magnetic Beads | Spike protein RBD antibody screening | |
| MBS-K013 | Human ACE2-coupled Magnetic Beads | Virus capture | |
| MBS-K014 | Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Antibody-coupled Magnetic Beads | Virus capture |
>>> References
[1] COVID-19 Map, Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center, 27 Aug 2021. Retrieved from https://coronavirus.jhu.edu /map.html
[2] WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data, World Health Organization, 27 Aug 2021. Retrieved from https://covid19.who.int/
[3] 7 Vaccines Approved for Use by WHO, COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker. Retrieved from https://covid19.trackvaccines.org /agency/who/
[4] Scudellari M. How the coronavirus infects cells — and why Delta is so dangerous. Nature (28 July 2021). Retrieved from https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02039-y
[5] Andersen, K.G., Rambaut, A., Lipkin, W.I. et al. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat Med 26, 450‒452 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.