 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?  Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
> Cardiac-related Solutions & Services
Explore our cardiac organoid products and services and how we can assist with cardiac modeling, organoid identification, and drug screening / testing. We now offer ready-to-use cardiac organoids, cardiac organoid differentiation services, and testing services that includes cell activity assays and electrophysiological studies.
Cardiac models play a pivotal role in studying heart-related conditions and assessing drug toxicity under cardiac-related conditions. Since cardiotoxicity testing is a prerequisite before clinical studies, using a relevant cardiac model is essential. We offer a wide range of products and services that encompass cardiac disease modeling, cardiac organoid identification, and drug screening services using cardiac organoid disease models.
Cardiac Organoids
Cardiac organoids are a miniaturized, in vitro version of the heart that is derived from either induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) or tissue fragments. These organoids are designed to have a similar cellular composition and architecture as the heart, while exhibiting similar mechanophysiological and electrophysiological properties. As such, cardiac organoids are a critical tool for researchers developing treatments for cardiovascular diseases, driving different applications such as:
Cardiotoxicity
Screening
Cardiotoxicity
Screening
Cardiac organoids derived from human cells mimic native heart tissue and functional properties resulting in a scalable, high-throughput drug screening assay.
Cardiac Disease
Modeling
Cardiac Disease
Modeling
Cardiac organoids derived from human cells mimic native heart tissue and functional properties resulting in a scalable, high-throughput drug screening assay.

Personalized Drug
Screening
Personalized Drug
Screening
Cardiac organoids derived from human cells mimic native heart tissue and functional properties resulting in a scalable, high-throughput drug screening assay.
Ready-to-use cardiac organoids are differentiated using our cardiac organoid kit (Ca. No. RIPO-HWM002K) and are designed to assist with drug efficacy and safety evaluations, as well as pharmacological research.
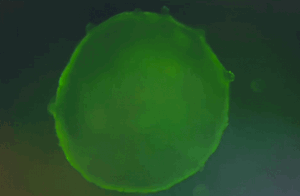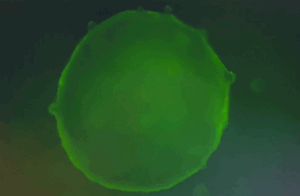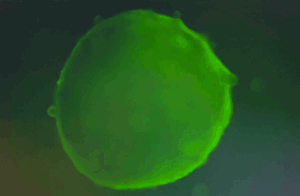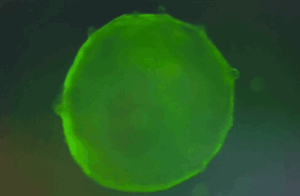
Cardiac organoids differentiated using the Human iPSC-Derived Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Kit (Ca. No. RIPO-HWM002K) show regular beating from day 7-13 of differentiation and calcium imaging.
| Cat. No. | Description |
| CIPO-HWL002K | Ready-to-use Human iPSC-derived Cardiac Organoids |
| RIPO-HWM002K | Human iPSC-derived Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Kit |
| RIPO-HWM004 | Human iPSC-derived Cardiac Organoid Maintenance Kit |
| RIPO-HWM005 | Cardiac Organoid Cryopreservation Kit |
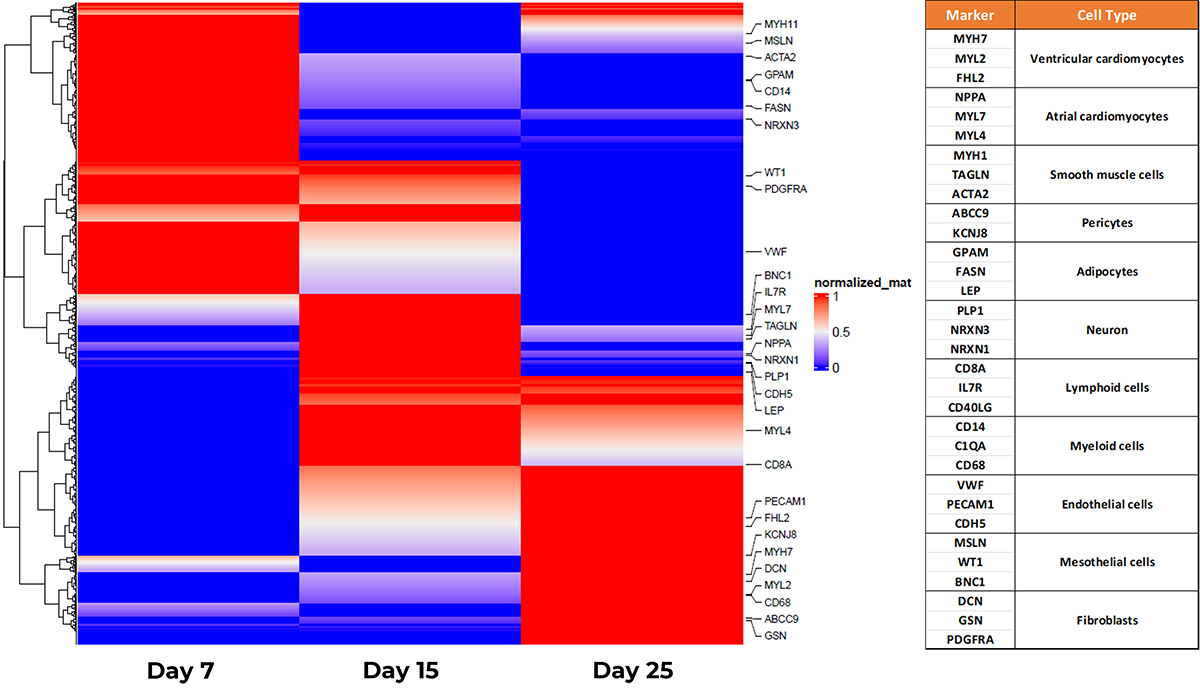
scRNA Sequencing of Cardiac Organoid at Different Stages. Cardiac organoids from the same batch were sequenced at different stages: (left) Day 7, (middle) Day 15), (right) Day 25. Depending on the maturation stage, the cellular composition of organoids can differ revealing a diverse cell population that matches what has been reported by S. Mendjan, et al.
Schmidt C, Deyett A, Mendjan S, et al. Multi-chamber cardioids unravel human heart development and cardiac defects. Cell. 2023 Dec 7;186(25):5587-5605.e27.
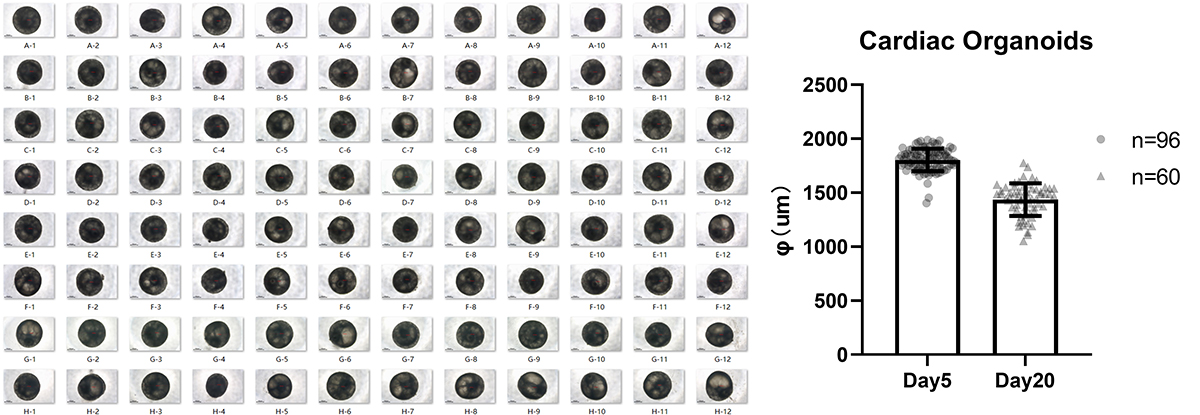
Organoid Batch Size Comparison. 96 organoids were photographed and calculated according to the resulting image. Organoid size is consistent with minimal deviation between the calculated radius of each of the derived organoids on day 5 and day 20.
Cardiac Cells
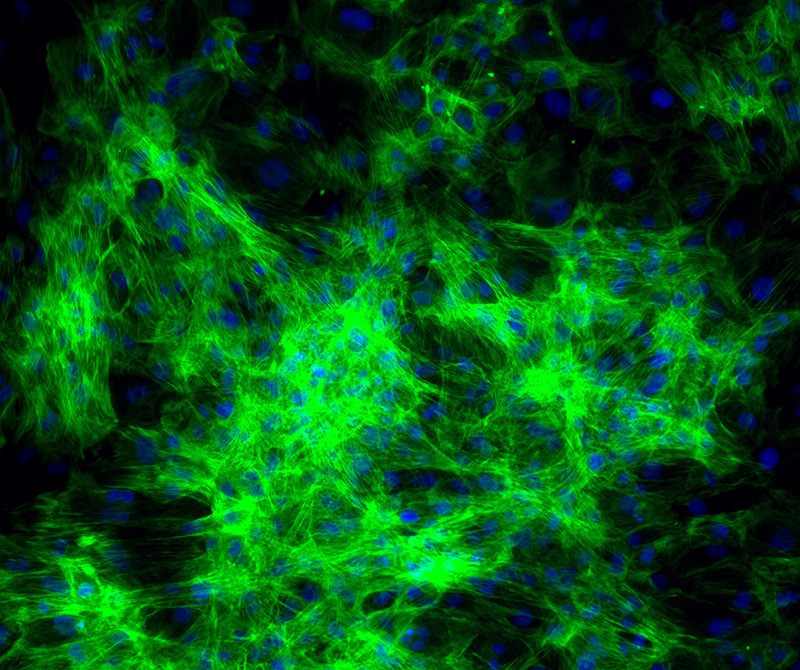
iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes validated with cardiac troponin (cTnT) can be provided for your studies into various cardiac-related diseases. This cell line is designed for cardiotoxicity screening and evaluation of electrical signal propagation through cardiomyocytes.
Interested? Leave a message!
Cardiac Services
We also provide various study services related to organoids differentiation, identification, and safety evaluations. This encompasses multiple molecular experimental platforms such as western blot, immunofluorescence, and qPCR. Our relioable electrophysiological platform using microelectrode arrays and patch clamps enables us to evaluate cardiac viability through the visualization of electric signal propogation derived from ion channel fucntion and ion uptake.
We offer differentiation services to develop cardiac organoids from iPSCs or human tissue. Organoids are validated by the expression of heart-related protein markers to ensure differentiation and maturity.
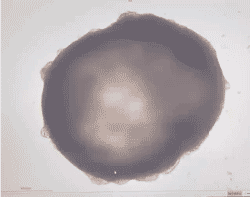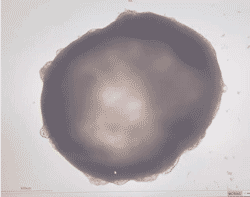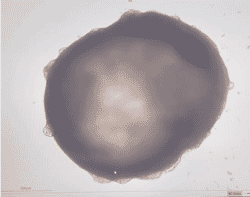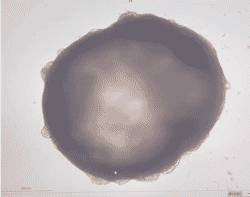
We can help measure the inhibitory effect of ion-channel blocking drugs (such as hERG potassium channels) on cardiomyocytes to better predict drug cardiotoxicity.
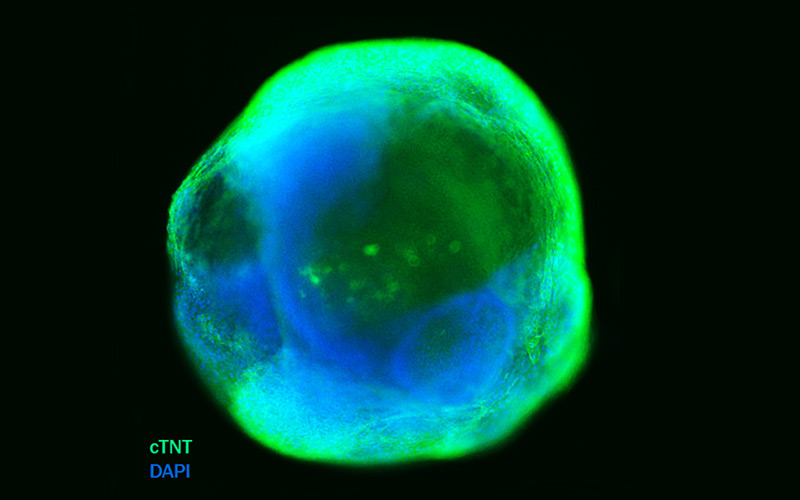
We can help construct a heart-failure model using our cardiac organoids derived from iPSCs for high-thoroughput drug candidate testing to screen for the ideal drug candidates.
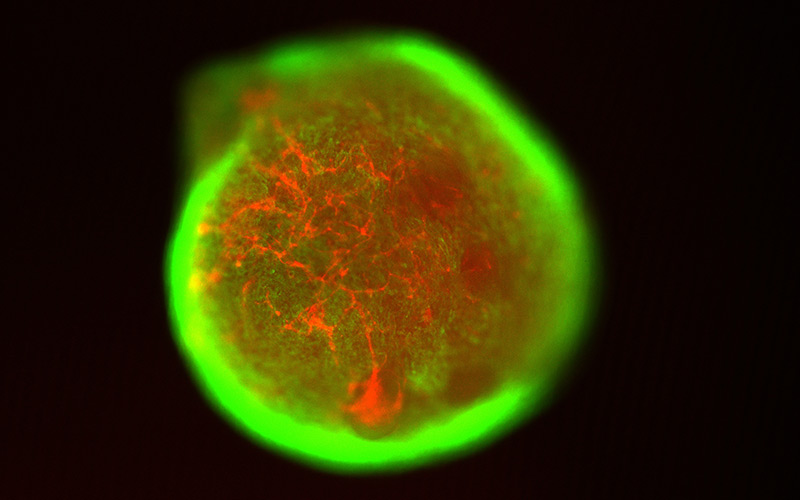
Cardiac Case Studies
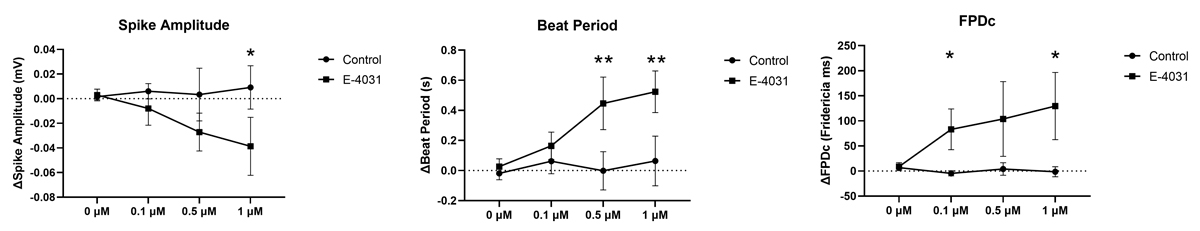
Several cardiac organoids were spiked with varying concentrations of E-4031, a selective hERG potassium channel blocker.
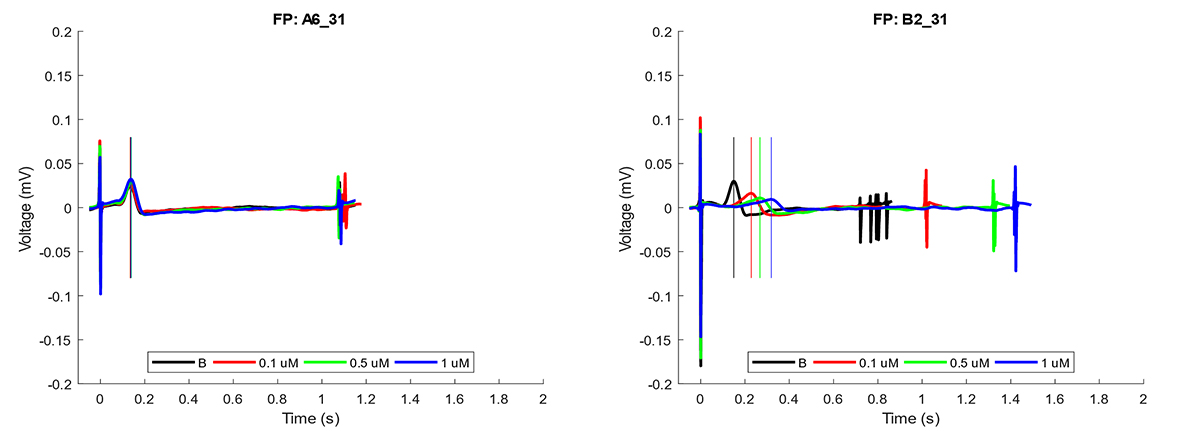
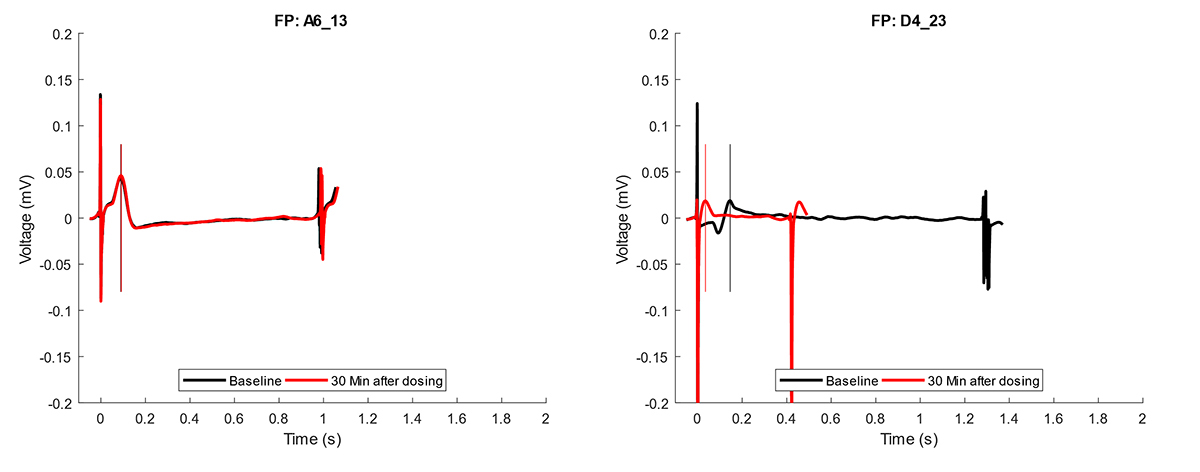
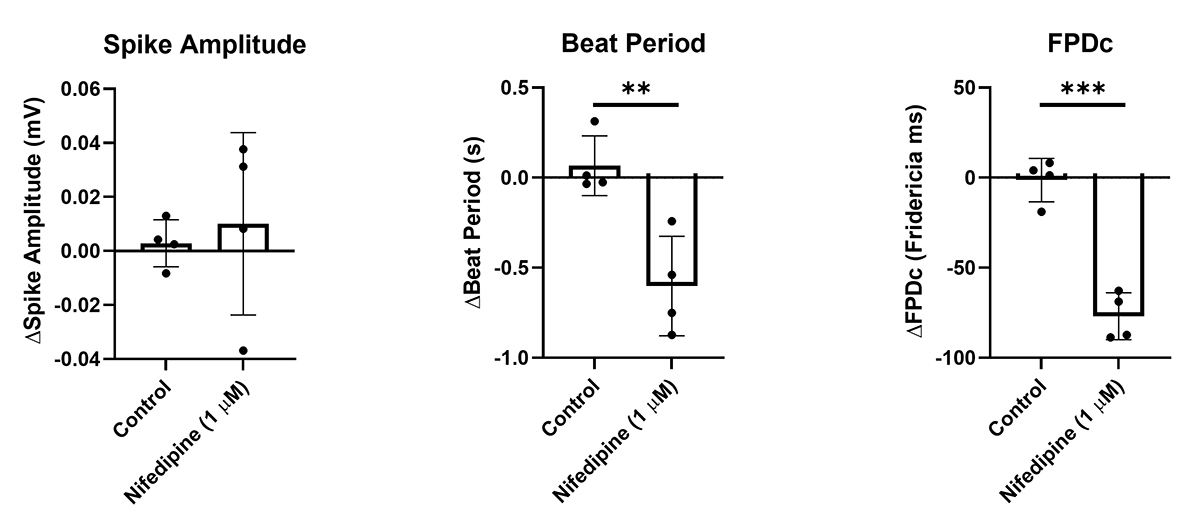
Cardiac organoids were treated with Nifedipine (1uM) and evaluated after 30 minutes using MEA. Nifedipine is a calcium channel blocker that leads to a shortened QT interval.
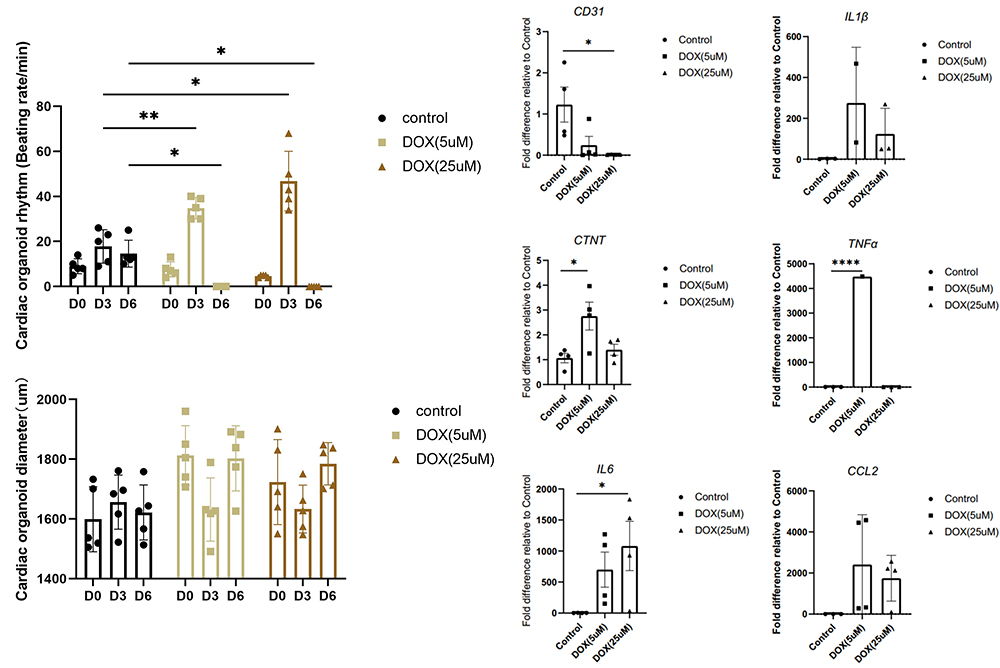
Cardiac organoids were dosed with DOX at different concentrations and observed over six days. Beat rhythm and diameter was evaluated by microscope before testing for released cytokines and CD31 expression by qPCR.
References
1. Blinova et al., 2017, Toxicol Sci (about CiPA iPSC-CM benchmark| Performance)
2. Hofbauer, P., Jahnel, S.M., Papai, N., et al. Cardioids reveals self-organizing principles of human cardiogenesis. Cell (2021), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.034
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.