 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?  Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
> Insights > 【Inspiring Target】CXCR4 and CCR5, Promising Targets for HIV and Tumor Therapy Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection is a viral infection that progressively destroys certain leukocytes and causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). After HIV enters the human body, it selectively attacks human immune cells (mainly CD4+ T lymphocytes). With the massive death of immune cells, the normal function of the human immune system is depleted and eventually destroyed. Ultimately AIDS patients will be susceptible to various diseases, opportunistic infections, and malignancies. Even though HIV is a multifactorial disease, studies have shown that specific targeting of CXCR4 and CCR5 is a promising therapeutic strategy for HIV as well as other immune conditions such as tumors.
CXCR4 belongs to the family of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). CXCR4 is a seven-transmembrane protein with a total length of 352 amino acids, which constitutes a circuitous surface receptor consisting of -NH2 outside and -COOH inside. The gene encoding CXCR4 is located on human chromosome 2q21 and is mainly expressed in monocytes, neutrophils, lymphocytes and activated T cells.
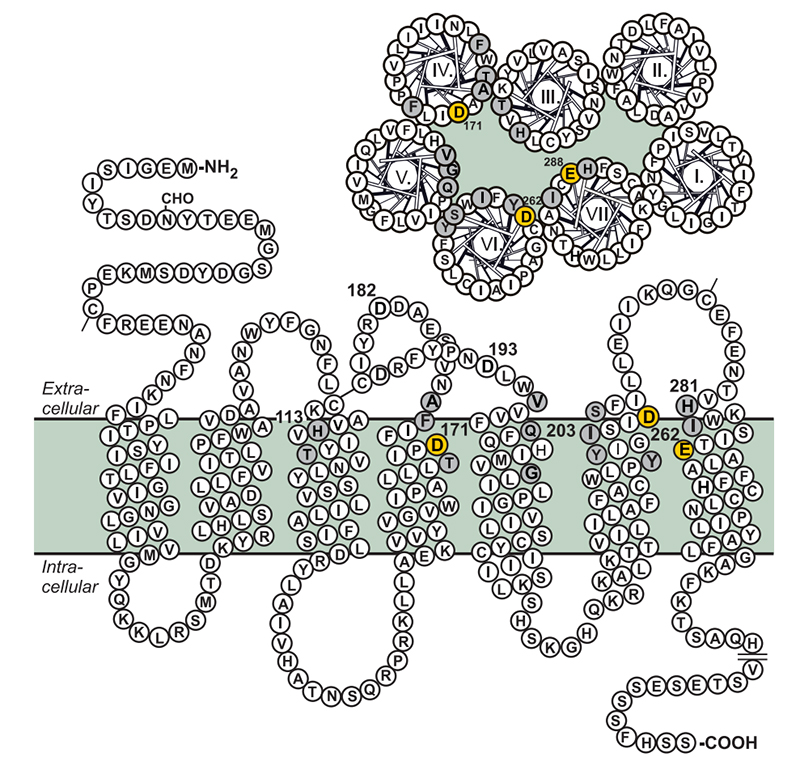
Structure of CXCR4
CXCR4 plays an important role in embryonic development, cell migration, angiogenesis, immune response, stem cell homing, inflammatory response, tumor growth and metastasis by binding to the specific ligand CXCL12 (SDF). CXCR4 knockout mice exhibited embryonic lethality and defects in vascular development, hematopoiesis, and Cardiac defect, further demonstrating the important physiological role of CXCR4.

Signaling pathway of CXCR4
CXCR4 acts as a co-receptor for HIV by binding CD4 protein, supporting HIV entry into the cells. As shown in the figure below, gp120 on the HIV viral membrane plays a key role in infecting CD4 T cells. When gp120 binds to the receptor CD4, it must also bind to a co-receptor such as CXCR4 to enter the cell. Therefore, CXCR4 antagonists are often used in HIV treatment.
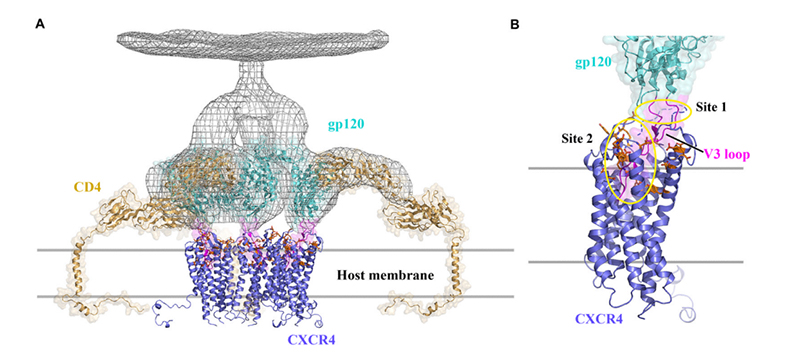
Structural model of CXCR4 interacting with CD4 to mediate HIV-1 entry into cells
Since CXCR4 can regulate the migration of hematopoietic stem cells, it may play an important role in bone marrow hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in clinic. In addition, CXCR4 is highly expressed in a variety of cancers, and its expression has been detected in differently originated 23 types of cancers. The overexpression of CXCR4 in tumor cells contributes to tumor growth, invasion, angiogenesis, metastasis, recurrence and Resistant. CXCR4 antagonists have been shown to disrupt tumor-stromal interactions, sensitize cancer cells to cytotoxic drugs, and reduce tumor growth and metastatic burden. Therefore, targeting CXCR4 is considered a promising therapeutic strategy.
Several drugs targeting CXCR4 are currently under development and are mainly small molecular antagonists, antibody drugs, gene therapy, and CAR-T therapy. Plerixafor (Mozobil), a small molecular antagonist targeting CXCR4, is on the market. Ulocuplumab, an antibody-drug developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb, is currently in Phase II clinical trials. This drug mainly treats leukemia, multiple myeloma, and WHIM syndrome.
Like CXCR4, CCR5 (C-C motif chemokine receptor 5) is also a member of the chemokine receptor family and GPCRs family, mainly expressed by T cells and macrophages. When combined with chemokine ligands, it increases intracellular calcium levels by activating downstream G proteins and other signaling molecules, thereby transducing signals.
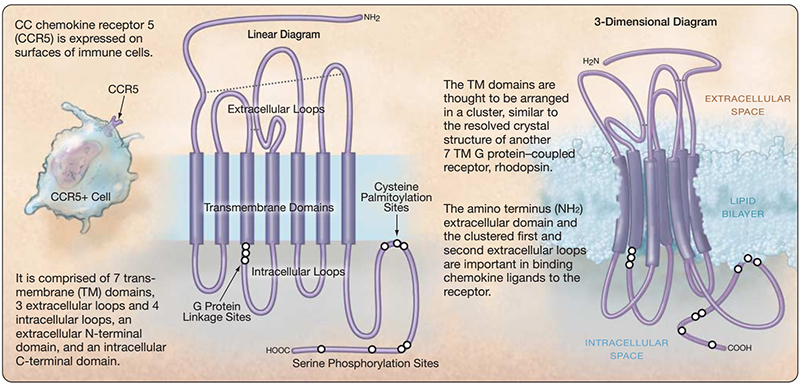
Structure of CCR5
CCR5 is an important co-receptor for HIV entering host cells, and this gene defect correlates with HIV infection tolerance. Therefore, CCR5 is an excellent target for HIV treatment. On February 15, 2022, the third case in the world who achieved long-term remission of AIDS - "New York patient" appeared. At the 29th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) in Denver, USA, a research team from Weill Cornell Medical College reported a case: a New York City patient with HIV and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has become the world's first woman and third person to be cured from AIDS to date. The patient had received CCR5 Δ32/Δ32 stem cell transplantation from a donor who is naturally resistant to HIV.

Chemokine receptors(CCR5 and CXCR4) mediate HIV entry into cells
Small molecule antagonists targeting CCR5 prevent HIV from interacting with the receptor mainly by binding to hydrophobic residues of CCR5. Maraviroc developed by Pfizer and GSK is the first small-molecule anti-HIV oral drug, a CCR5 receptor antagonist, with the trade name Selzentry. The FDA approved the drug on August 6, 2007, EMA on September 18, 2007, and PMDA on December 25, 2008. In addition to CCR5 small molecule antagonists, monoclonal antibodies, gene therapy and T cell therapy for HIV treatment targeting CCR5 are under different stages of development.
Meanwhile, CCR5 is widely expressed on tumors plays an important role in the occurrence and development of tumors. CCR5 is also an exciting new therapeutic target for treating metastatic cancer.
ACROBiosystems is focused on overcoming the challenges during the preparation of GPCRs. We provide full-length GPCRs proteins via "FLAG" technology platforms to assist our customers and collaborators with antibody drugs and therapeutic strategies. Recently, full-length CCR5 and CXCR4 proteins have been developed and launched, do not hesitate to consult and order.
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Species | Product Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| CXCR4 | CX4-H5219 | Human | Human CXCR4 / CD184 Full Length Protein-VLP (HEK293)NEW |
| CCR5 | CC5-H52P3 | Human | Human CCR5 Full Length Protein-VLP (HEK293)NEW |
![]() Full-length CCR5 and CXCR4 proteins are with native and complete conformation
Full-length CCR5 and CXCR4 proteins are with native and complete conformation
![]() Higher immunogenicity due to inherent characteristics of VLP
Higher immunogenicity due to inherent characteristics of VLP
![]() High biological activity verified by binding to antibodies
High biological activity verified by binding to antibodies
![]() 100-300 nm in size and high identity verified by DLS, can be used as an optimal target for dendritic cells and phage display
100-300 nm in size and high identity verified by DLS, can be used as an optimal target for dendritic cells and phage display
![]() Suitable for immunization/ELISA/SPR/BLI/cell experiment etc.
Suitable for immunization/ELISA/SPR/BLI/cell experiment etc.

Immobilized Human CXCR4 Full Length Protein-VLP (Cat. No. CX4-H5219) at 5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human ulocuplumab, Human IgG4 with a linear range of 1-31 ng/mL (QC tested).

The mean peak Radius of CXCR4-VLP is 110-170 nm with more than 95% intensity as determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS).

Immobilized Human CCR5 Full Length Protein-VLP (Cat. No. CC5-H52P3) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Anti-Human CCR5 Antibody, Mouse IgG2a with a linear range of 2-78 ng/mL (QC tested).

The mean peak Radius of CCR5-VLP is 130-170 nm with more than 95% intensity as determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS).
>>> Learn more about “FLAG”: full-length multi-pass transmembrane proteins and technology platforms
1. Guido Lancman1, Dahniel L. Sastow,et al. Bispecifc Antibodies in Multiple Myeloma: Present and Future. Blood Cancer Discov 2021, 2:423–33. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-21-0028
2. Lederman MM, Penn-Nicholson A, Cho M, Mosier D. Biology of CCR5 and its role in HIV infection and treatment. JAMA. 2006, 296(7):815-26. doi: 10.1001/jama.296.7.815. PMID: 16905787.
3. Fedora Grande, Maria Antonietta Occhiuzzi, Bruno Rizzuti et al. CCR5/CXCR4 Dual Antagonism for the Improvement of HIV Infection Therapy. Molecules. 2019, 24(3), 550; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030550
4. Blanpain C, Migeotte I, Lee B, Vakili J, Doranz BJ, Govaerts C, Vassart G, Doms RW, Parmentier M. CCR5 binds multiple CC-chemokines: MCP-3 acts as a natural antagonist. Blood. 1999, 94(6):1899-905. PMID: 10477718.
5. Tagliamonte M, Tornesello ML, Buonaguro FM, Buonaguro L. Conformational HIV-1 envelope on particulate structures: a tool for chemokine coreceptor binding studies. J Transl Med. 2011 ,27;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1): S1. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-S1-S1. PMID: 21284899; PMCID: PMC3105500.
6. Barmania F, Pepper MS. C-C chemokine receptor type five (CCR5): An emerging target for the control of HIV infection. Appl Transl Genom. 2013(2):3-16. doi: 10.1016/j.atg.2013.05.004. PMID: 27942440; PMCID: PMC5133339.
7. Jiao X, Nawab O, Patel T, Kossenkov AV, Halama N, Jaeger D, Pestell RG. Recent Advances Targeting CCR5 for Cancer and Its Role in Immuno-Oncology. Cancer Res. 2019, 79(19):4801-4807. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1167. Epub 2019 Jul 10. PMID: 31292161; PMCID: PMC6810651.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.