 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!  Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
 Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?  Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
Thank you for choosing ACROBiosystems. Would you rate our product and service?
 Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!  Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
Here come GMP Grade Cytokines!Free Sample is available!
> News > SEC-MALS: Accurate Determination of Protein Molecular Weight and Confirmation of Polymer State Recombinant protein antigens are involved in various R&D processes, including antibody-drug development, pre-immunization, antibody screening, identification, antibody-drug candidate function verification in vivo and in vitro, quality control, and clinical sample analysis. The quality and activity of the recombinant protein can have a tremendous impact on the success and even cycle of antibody-drug development.
Recombinant protein antigens must maintain correct folding and consistent conformation with the native proteins. Therefore, ensuring the natural activity of the protein antigens and minimal batch-to-batch inconsistency, will ensure a high success rate of drug development. As an industry leader in recombinant proteins for drug development, ACROBiosystems is committed to "Where Proteins and Innovation Advance Biomedicine." Our company's commitment extends beyond recombinant protein design, expression, and production process of strict control into an established, accurate, and reliable molecular weight determination analysis method. Our methods can accurately characterize the aggregation state of recombinant proteins under physiological conditions in solution and guide the design, production process optimization, and quality control of recombinant protein antigen products.
Several methods are used to analyze molecular protein weight, including:
(1) An interpolation method based on SEC-HPLC (High-Performance Molecular Sieve Liquid Chromatography) to estimate the retention time;
(2) Molecular weight absolute quantification based on SEC-MALS (Multi-angle Laser Scattering).
Both techniques can determine the molecular weight of proteins in solution, but there are some differences in principle. The similarities and differences between the two techniques are as follows:
| Detection method | Principles and features | Results |
|---|---|---|
| SEC-HPLC | Column correction method | Calculate the relative molecular weight by comparing the elution retention times of the protein to be measured and the standard protein |
| It is assumed that the conformation of the protein to be measured is similar in shape to the standard protein. It is assumed that there is no non-specific interaction with the column packing, and each elution time is reproducible without drift | ||
| SEC-MALS | Light scattering method | Absolute molecular weight was determined directly by laser scattering intensity. Molecular weight determination was independent of elution volume or retention time. |
| The intensity of the scattered light is proportional to the square of the molar mass, concentration, and refractive index increment. The angular dependence of scattering light is only dependent on the size of the molecule. |
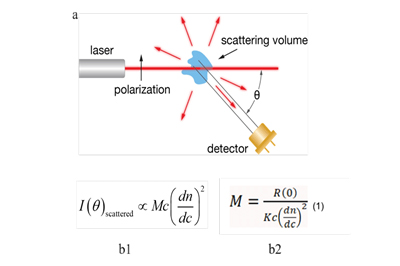
Fig 1. Schematic diagram of SEC-MALS detection a. Light scattering sketch b. Molecular weight calculation of analytes
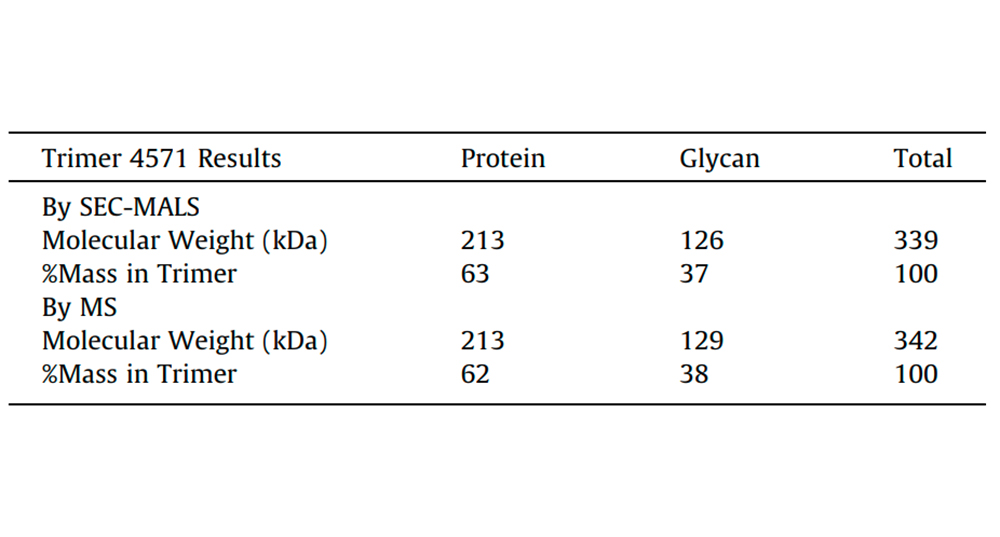
Fig. 2. Comparison of Trimer 4571 molecular weight results obtained by SEC-MALS with MS data
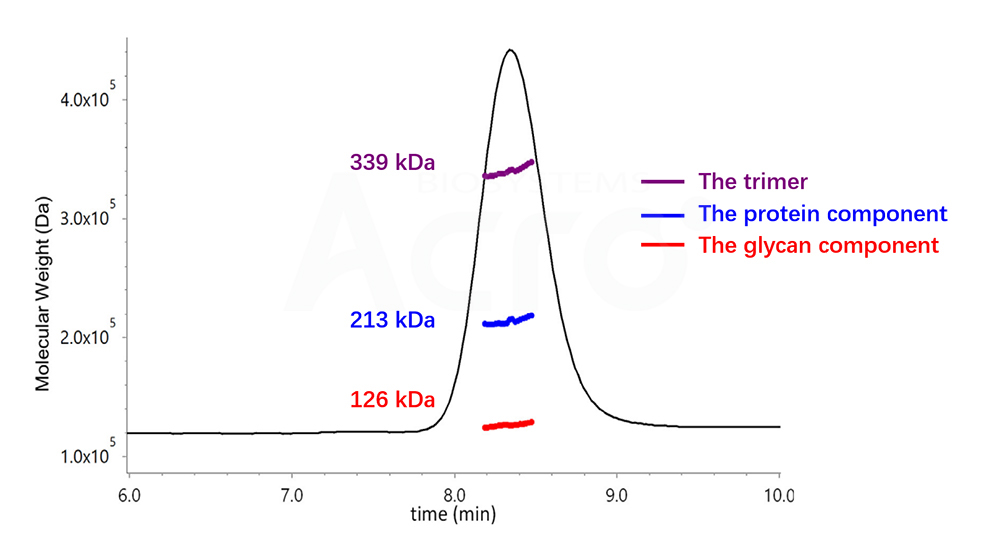
Fig 3. Determination of Trimer by SEC-UV-dRI-MALS
| Antibody Name | Column | Retention time TR (min) | Molecular weight (SEC-HPLC) | Molecular weight (SEC -MALS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OKT3 | G3000SWxl | 14.775 | 212.5 kDa | 161.6 kDa |
| Herceptin | G3000SWxl | 15.436 | 146 kDa | 151 kDa |
| lpilimumab | G3000SWxl | 17.039 | 66.3 kDa | 172.2 kDa |
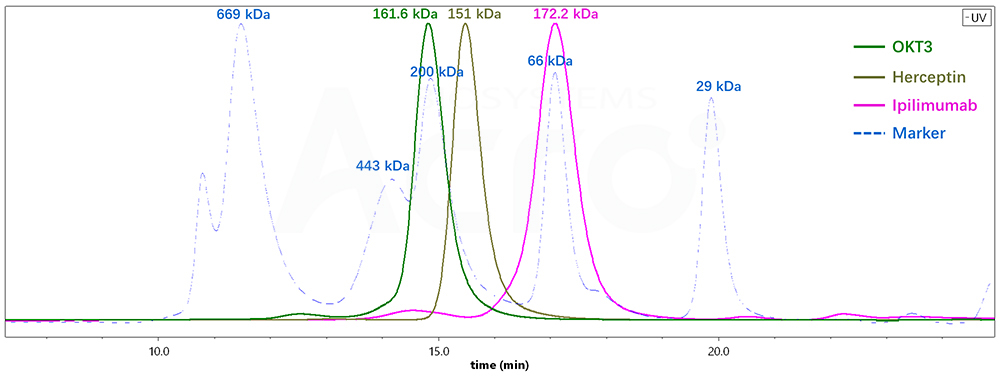
Fig 4. Molecular weight determination of different antibodies by SEC-HPLC
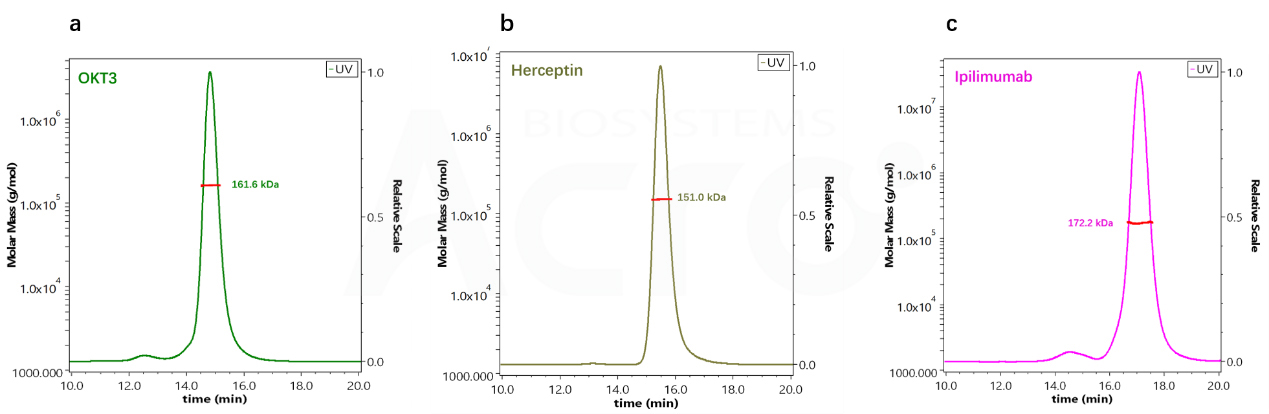
Fig 5. Determination of Molecular Weight of Three Antibody Drugs by SEC-MALS
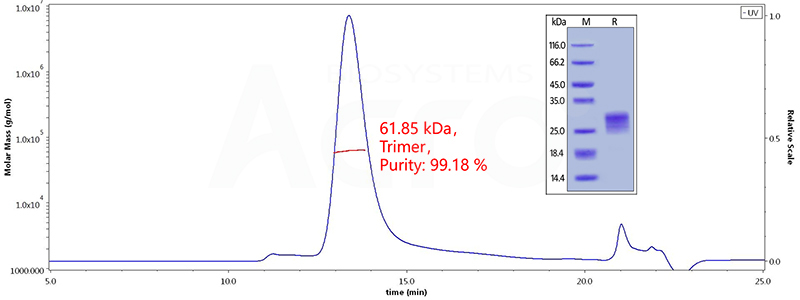
Figure 6. The purity of Human OX40 Ligand, His Tag (active trimer) (Cat. No. o. OXL-H52Q8 ) is more than 95% in HP-SEC, and the molecular weight of this protein is around 60-80 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
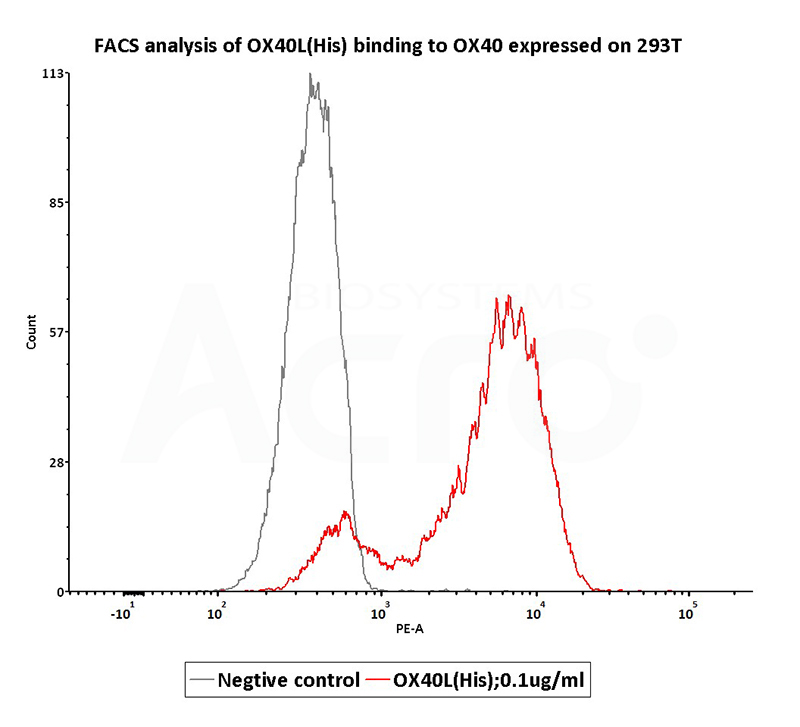
Figure 7. FACS analysis shows that human sources OX40 Ligand, His Tag (active trimer) (Cat. No. OXL-H52Q8 ) can bind to 293T cells overexpressing human OX40. The concentration of OX40 Ligand was 0.1 μg / mL.
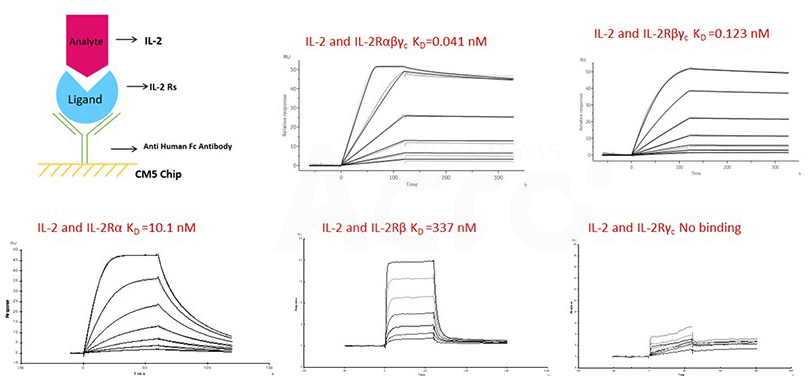
Fig 10. SPR verified the binding affinity of IL-2 to ACRO's IL-2R construct.
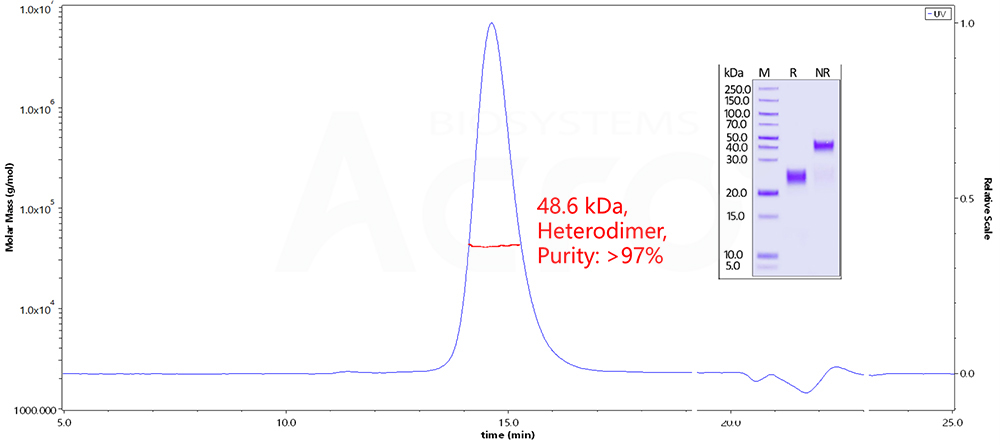
Fig 11. The purity of Human CTLA-4, His Tag (Cat. No. CT4-H52H9 ) is more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 45-60 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
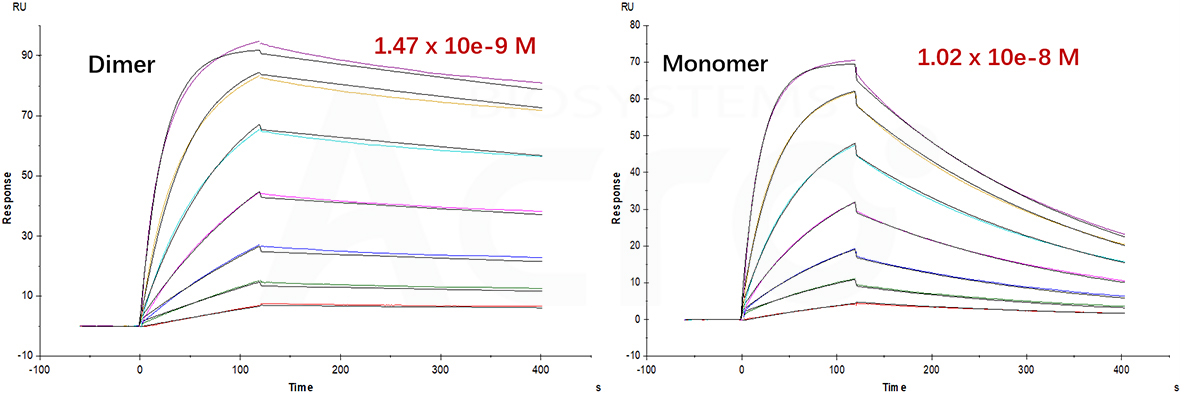
Fig 12. SPR verified that the affinity of CTLA-4 dimer is more than ten times higher than that of monomer
Cat. No. SPN-C52H9(SARS-CoV-2 S protein, His Tag, Super stable trimer (MALS & NS-EM verified))
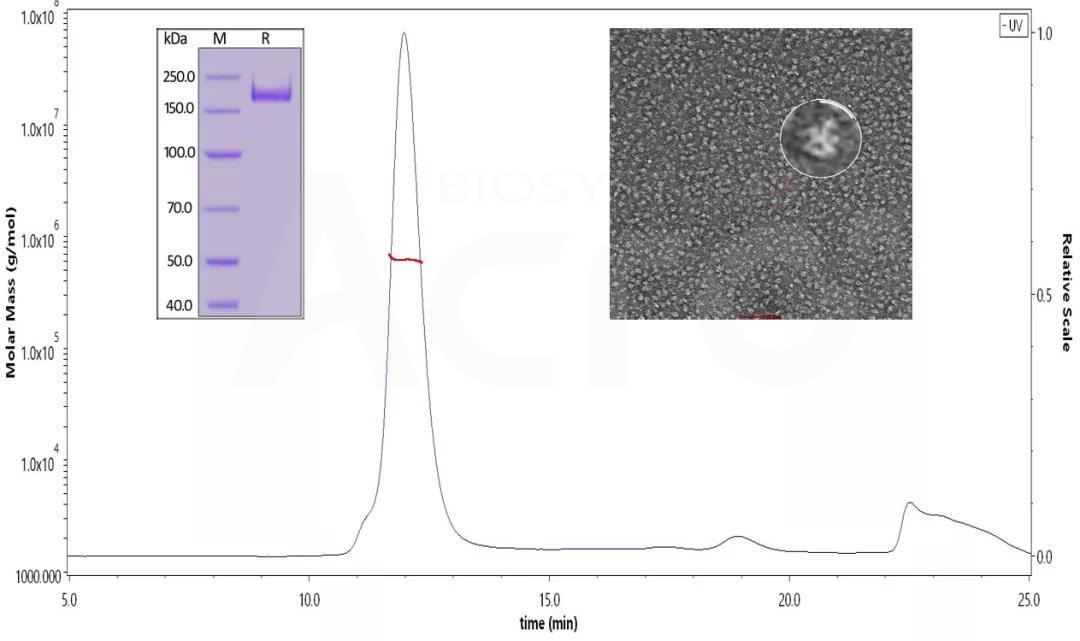
Fig 13. SDS-PAGE identified the SARS-CoV-2 S protein under reduced conditions. His Tag, Super stable trimer (MALS & NS-EM verified) (Cat. No. SPN-C52H9 ) The purity is over 90%, and the molecular weight is about 550-660 kDa by SEC-MALS. The size and appearance of the SARS-CoV-2 trimer verified with NS-EM were like those reported in the published literature.
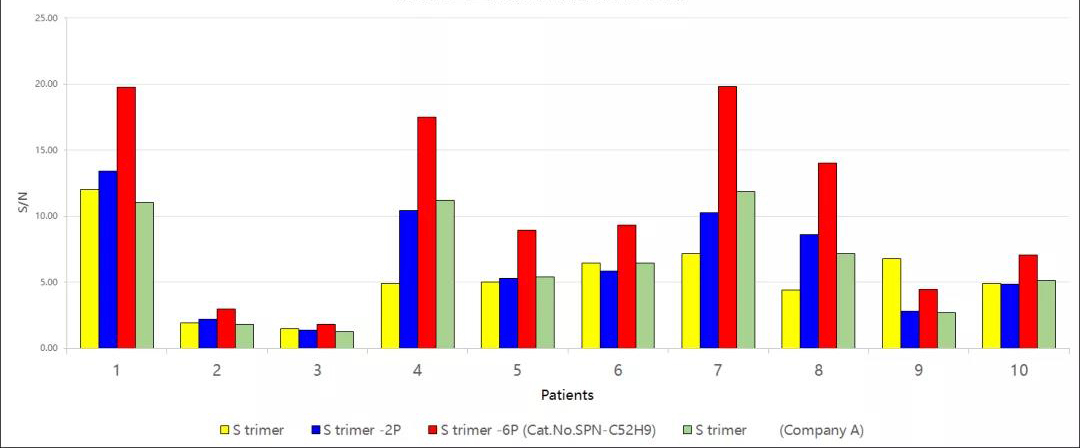
Fig 14. Comparative analysis of antibody titers of serum samples from rehabilitated patients detected by S-6P protein, S-2P protein, and S protein. The results showed that the signal-to-noise ratio of S-6P was significantly higher than that of S protein, S-2P, and other S proteins. It suggested that S-6P was more suitable for antibody titer detection in serum samples and could detect antibody titers in serum early after injection of vaccine, which was helpful for evaluation of vaccine immunogenicity.
CD3E&CD3D
(Star products: Cat. No. CDD-H52Wa)
LRRC32&TGF beta-1
(Star products: Cat. No.GA1-H52W9)
CD73
(Star products: Cat. No.CD3-S52H3)
FAP protein
(Star products: Cat. No.FAP-H5244)
PSMA
(Star products: Cat. No.PSA-H52H3)
TIGIT
(Star products: Cat. No.TIT-H52H5)
CD79A&CD79B
(Star products: Cat. No.CDB-H52W3)
IL-17A & IL-17F
(Star products: Cat. No.ILF-H52W6)
IL23A & IL12B
(Star products: Cat. No.ILB-HR52W3)
Integrin alpha 2 beta 1
(Star products: Cat. No.IT1-M52W3)
TNFSF
CD3
FcRn (FCGRT & B2M)
Interleukin
Spike trimer
Others
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure |
|---|
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure |
|---|
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure |
|---|
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure |
|---|
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure |
|---|
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure |
|---|
[1]Bender M F , Li Y , Ivleva V B , et al. Protein and glycan molecular weight determination of highly glycosylated HIV-1 envelope trimers by HPSEC-MALS[J]. Vaccine, 2021(7523).
[2]Sriram B , Tania C R , Davis A M , et al. Ligand binding kinetics of IL-2 and IL-15 to heteromers formed by extracellular domains of the three IL-2 receptor subunits[J]. International Immunology(11):1839.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.